Attributes
The table below describes the attributes used by various Graphviz tools. The table gives the name of the attribute, the graph components (node, edge, etc.) which use the attribute and the type of the attribute (strings representing legal values of that type). Where applicable, the table also gives a default value for the attribute, a minimum allowed setting for numeric attributes, and certain restrictions on the use of the attribute.
Note that attribute names are case-sensitive. This is usually true for attribute values as well, unless noted.
All Graphviz attributes are specified by name-value pairs. Thus, to
set the color of a node abc, one would use
Similarly, to set the arrowhead style of an edge abc -> def,
one would use:
Further details concerning the setting of attributes can be found in the description of the DOT language.
At present, most device-independent units are either inches or points, which we take as 72 points per inch.
Note: Some attributes, such as
dir or arrowtail, are ambiguous when used in
DOT with an undirected graph since the head and tail of an edge
are meaningless. As a convention, the first time an undirected edge appears,
the DOT
parser will assign the left node as the tail node and the right node as
the head. For example, the edge A -- B will have tail A
and head B. It is the user’s responsibility to handle such
edges consistently. If the edge appears later, in the format
the drawing will attach the tail label to node A.
To avoid possible confusion when such attributes are required, the user
is encouraged to use a directed graph.
If it is important to make the graph appear undirected, this can be
done using the dir, arrowtail or
arrowhead attributes.
The tools accept standard C representations for int and
double types.
For the bool type, TRUE values are
represented by true or yes (case-insensitive)
and any non-zero integer, and FALSE values by false or no (case-insensitive)
and zero.
In addition, there are a variety of specialized types such as
arrowType, color,
point and rankdir. Legal values for these types are given
at the end.
In the Used By field, the
characters E, N, G, S and C
represent edges, nodes, the root graph, subgraphs
and cluster subgraphs, respectively.
This field indicates which graph component uses the attribute.
In the Notes field, an annotation of write only indicates that the attribute is used for output, and is not used or read by any of the layout programs.
| Name | Used By | Type | Default | Minimum | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
_background |
G | string | <none> |
||
area |
NC | double | 1.0 |
>0 |
patchwork only |
arrowhead |
E | arrowType | normal |
||
arrowsize |
E | double | 1.0 |
0.0 |
|
arrowtail |
E | arrowType | normal |
||
bb |
G | rect | write only | ||
bgcolor |
GC | color colorList |
<none> |
||
center |
G | bool | false |
||
charset |
G | string | "UTF-8" |
||
class |
ENCG | string | "" |
svg only | |
clusterrank |
G | clusterMode | local |
dot only | |
color |
ENC | color colorList |
black |
||
colorscheme |
ENCG | string | "" |
||
comment |
ENG | string | "" |
||
compound |
G | bool | false |
dot only | |
concentrate |
G | bool | false |
||
constraint |
E | bool | true |
dot only | |
Damping |
G | double | 0.99 |
0.0 |
neato only |
decorate |
E | bool | false |
||
defaultdist |
G | double | 1+(avg. len)*sqrt(|V|) |
epsilon |
neato only |
dim |
G | int | 2 |
2 |
neato, fdp, sfdp only |
dimen |
G | int | 2 |
2 |
neato, fdp, sfdp only |
dir |
E | dirType | forward (directed) none (undirected) |
||
diredgeconstraints |
G | string bool |
false |
neato only | |
distortion |
N | double | 0.0 |
-100.0 |
|
dpi |
G | double | 96.00.0 |
bitmap output, svg only | |
edgehref |
E | escString | "" |
map, svg only | |
edgetarget |
E | escString | <none> |
map, svg only | |
edgetooltip |
E | escString | "" |
cmap, svg only | |
edgeURL |
E | escString | "" |
map, svg only | |
epsilon |
G | double | .0001 * # nodes (mode == KK)' .0001 (mode == major) .01 (mode == sgd) |
neato only | |
esep |
G | addDouble addPoint |
+3 |
not dot | |
fillcolor |
NEC | color colorList |
lightgrey (nodes) black (clusters) |
||
fixedsize |
N | bool string |
false |
||
fontcolor |
ENGC | color | black |
||
fontname |
ENGC | string | "Times-Roman" |
||
fontnames |
G | string | "" |
svg only | |
fontpath |
G | string | <system-dependent> |
||
fontsize |
ENGC | double | 14.0 |
1.0 |
|
forcelabels |
G | bool | true |
||
gradientangle |
NCG | int | "" |
||
group |
N | string | "" |
dot only | |
head_lp |
E | point | write only | ||
headclip |
E | bool | true |
||
headhref |
E | escString | "" |
map, svg only | |
headlabel |
E | lblString | "" |
||
headport |
E | portPos | center |
||
headtarget |
E | escString | <none> |
map, svg only | |
headtooltip |
E | escString | "" |
cmap, svg only | |
headURL |
E | escString | "" |
map, svg only | |
height |
N | double | 0.5 |
0.02 |
|
href |
GCNE | escString | "" |
map, postscript, svg only | |
id |
GCNE | escString | "" |
map, postscript, svg only | |
image |
N | string | "" |
||
imagepath |
G | string | "" |
||
imagepos |
N | string | "mc" |
||
imagescale |
N | bool string |
false |
||
inputscale |
G | double | <none> |
neato, fdp only | |
K |
GC | double | 0.3 |
0 |
fdp, sfdp only |
label |
ENGC | lblString | "\N" (nodes) "" (otherwise) |
||
label_scheme |
G | int | 0 |
0 |
sfdp only |
labelangle |
E | double | -25.0 |
-180.0 |
|
labeldistance |
E | double | 1.0 |
0.0 |
|
labelfloat |
E | bool | false |
||
labelfontcolor |
E | color | black |
||
labelfontname |
E | string | "Times-Roman" |
||
labelfontsize |
E | double | 14.0 |
1.0 |
|
labelhref |
E | escString | "" |
map, svg only | |
labeljust |
GC | string | "c" |
||
labelloc |
NGC | string | "t" (clusters) "b" (root graphs) "c" (nodes) |
||
labeltarget |
E | escString | <none> |
map, svg only | |
labeltooltip |
E | escString | "" |
cmap, svg only | |
labelURL |
E | escString | "" |
map, svg only | |
landscape |
G | bool | false |
||
layer |
ENC | layerRange | "" |
||
layerlistsep |
G | string | "," |
||
layers |
G | layerList | "" |
||
layerselect |
G | layerRange | "" |
||
layersep |
G | string | ":\t " |
||
layout |
G | string | "" |
||
len |
E | double | 1.0 (neato) 0.3 (fdp) |
neato, fdp only | |
levels |
G | int | MAXINT |
0.0 |
sfdp only |
levelsgap |
G | double | 0.0 |
neato only | |
lhead |
E | string | "" |
dot only | |
lheight |
GC | double | write only | ||
lp |
EGC | point | write only | ||
ltail |
E | string | "" |
dot only | |
lwidth |
GC | double | write only | ||
margin |
NCG | double point |
<device-dependent> |
||
maxiter |
G | int | 100 * # nodes (mode == KK) 200 (mode == major) 30 (mode == sgd) 600 (fdp) |
neato, fdp only | |
mclimit |
G | double | 1.0 |
dot only | |
mindist |
G | double | 1.0 |
0.0 |
circo only |
minlen |
E | int | 1 |
0 |
dot only |
mode |
G | string | major |
neato only | |
model |
G | string | shortpath |
neato only | |
mosek |
G | bool | false |
neato only | |
newrank |
G | bool | false |
dot only | |
nodesep |
G | double | 0.25 |
0.02 |
|
nojustify |
GCNE | bool | false |
||
normalize |
G | double bool |
false |
not dot | |
notranslate |
G | bool | false |
neato only | |
nslimit |
G | double | dot only | ||
nslimit1 |
G | double | dot only | ||
ordering |
GN | string | "" |
dot only | |
orientation |
NG | double string |
0.0"" |
360.0 |
|
outputorder |
G | outputMode | breadthfirst |
||
overlap |
G | string bool |
true |
not dot | |
overlap_scaling |
G | double | -4 |
-10000000000 |
prism only |
overlap_shrink |
G | bool | true |
prism only | |
pack |
G | bool int |
false |
||
packmode |
G | packMode | node |
||
pad |
G | double point |
0.0555 (4 points) |
||
page |
G | double point |
|||
pagedir |
G | pagedir | BL |
||
pencolor |
C | color | black |
||
penwidth |
CNE | double | 1.0 |
0.0 |
|
peripheries |
NC | int | <shape default> (nodes) 1 (clusters) |
0 |
|
pin |
N | bool | false |
neato, fdp only | |
pos |
EN | point splineType |
|||
quadtree |
G | quadType bool |
normal |
sfdp only | |
quantum |
G | double | 0.0 |
0.0 |
|
rank |
S | rankType | dot only | ||
rankdir |
G | rankdir | TB |
dot only | |
ranksep |
G | double doubleList |
0.5 (dot) 1.0 (twopi) |
0.02 |
dot, twopi only |
ratio |
G | double string |
|||
rects |
N | rect | write only | ||
regular |
N | bool | false |
||
remincross |
G | bool | true |
dot only | |
repulsiveforce |
G | double | 1.0 |
0.0 |
sfdp only |
resolution |
G | double | 96.00.0 |
bitmap output, svg only | |
root |
GN | string bool |
<none> (graphs) false (nodes) |
twopi, circo only | |
rotate |
G | int | 0 |
||
rotation |
G | double | 0 |
sfdp only | |
samehead |
E | string | "" |
dot only | |
sametail |
E | string | "" |
dot only | |
samplepoints |
N | int | 8 (output) 20 (overlap and image maps) |
||
scale |
G | double point |
not dot | ||
searchsize |
G | int | 30 |
dot only | |
sep |
G | addDouble addPoint |
+4 |
not dot | |
shape |
N | shape | ellipse |
||
shapefile |
N | string | "" |
||
showboxes |
ENG | int | 0 |
0 |
dot only |
sides |
N | int | 4 |
0 |
|
size |
G | double point |
|||
skew |
N | double | 0.0 |
-100.0 |
|
smoothing |
G | smoothType | "none" |
sfdp only | |
sortv |
GCN | int | 0 |
0 |
|
splines |
G | bool string |
|||
start |
G | startType | "" |
neato, fdp only | |
style |
ENCG | style | "" |
||
stylesheet |
G | string | "" |
svg only | |
tail_lp |
E | point | write only | ||
tailclip |
E | bool | true |
||
tailhref |
E | escString | "" |
map, svg only | |
taillabel |
E | lblString | "" |
||
tailport |
E | portPos | center |
||
tailtarget |
E | escString | <none> |
map, svg only | |
tailtooltip |
E | escString | "" |
cmap, svg only | |
tailURL |
E | escString | "" |
map, svg only | |
target |
ENGC | escString string |
<none> |
map, svg only | |
tooltip |
NECG | escString | "" |
cmap, svg only | |
truecolor |
G | bool | bitmap output only | ||
URL |
ENGC | escString | <none> |
map, postscript, svg only | |
vertices |
N | pointList | write only | ||
viewport |
G | viewPort | "" |
||
voro_margin |
G | double | 0.05 |
0.0 |
not dot |
weight |
E | int double |
1 |
0(dot,twopi)1(neato,fdp) |
|
width |
N | double | 0.75 |
0.01 |
|
xdotversion |
G | string | xdot only | ||
xlabel |
EN | lblString | "" |
||
xlp |
NE | point | write only | ||
z |
N | double | 0.0 |
-MAXFLOAT-1000 |
_background
type: string, default: <none>
A string in the xdot format specifying an arbitrary background.
During rendering, the canvas is first filled as described in the
bgcolor attribute.
Then, if _background is defined, the graphics
operations described in the string are performed on the canvas.
- Graphs
area
type: double, default: 1.0, minimum: >0
Indicates the preferred area for a node or empty cluster when laid out by patchwork.
- Clusters
- Nodes
arrowhead
type: arrowType, default: normal
Style of arrowhead on the head node of an edge.
This will only appear if the dir attribute
is forward or both.
See the limitation.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
arrowsize
type: double, default: 1.0, minimum: 0.0
Multiplicative scale factor for arrowheads.
- Edges
arrowtail
type: arrowType, default: normal
Style of arrowhead on the tail node of an edge.
This will only appear if the dir attribute
is back or both.
See the limitation.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
bb
type: rect
Bounding box of drawing in points.
Valid on:- Graphs
bgcolor
type: color | colorList, default: <none>
When attached to the root graph, this color is used as the background for entire canvas.
When a cluster attribute, it is used as the initial background
for the cluster. If a cluster has a filled style, the cluster’s
fillcolor will overlay the background color.
If the value is a colorList, a gradient fill is used. By
default, this is a linear fill; setting style=radial will
cause a radial fill. Only two colors are used. If the second color (after a
colon) is missing, the default color is used for it. See also the
gradientangle attribute for setting the gradient angle.
For certain output formats, such as PostScript, no fill is done for the root
graph unless bgcolor is explicitly set.
For bitmap formats, however, the bits need to be initialized to something, so
the canvas is filled with white by default. This means that if the bitmap
output is included in some other document, all of the bits within the
bitmap’s bounding box will be set, overwriting whatever color or graphics
were already on the page. If this effect is not desired, and you only want to
set bits explicitly assigned in drawing the graph, set
bgcolor="transparent".
- Clusters
- Graphs
center
type: bool, default: false
If true, the drawing is centered in the output canvas.
Valid on:- Graphs
charset
type: string, default: "UTF-8"
Specifies the character encoding used when interpreting string input as a text label.
The default value is "UTF-8". The other legal value is "iso-8859-1" or,
equivalently, "Latin1".
The charset attribute is case-insensitive.
Note that if the character encoding used in the input does not match the
charset value, the resulting output may be very strange.
- Graphs
class
type: string, default: ""
Classnames to attach to the node, edge, graph, or cluster’s SVG element.
Combine with stylesheet for styling SVG output
using CSS classnames.
Multiple space-separated classes are supported.
See also:
Example:
- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
clusterrank
type: clusterMode, default: local
Mode used for handling clusters. If clusterrank=local, a
subgraph whose name begins with cluster is given special treatment.
The subgraph is laid out separately, and then integrated as a unit into
its parent graph, with a bounding rectangle drawn about it.
If the cluster has a label parameter, this label
is displayed within the rectangle.
Note also that there can be clusters within clusters.
The modes clusterrank=global and clusterrank=none appear to
be identical, both turning off the special cluster processing.
- Graphs
color
type: color | colorList, default: black
Basic drawing color for graphics, not text. For the latter, use the
fontcolor attribute.
For edges, the value can either be a single color or a
colorList.
In the latter case, if colorList has no fractions,
the edge is drawn using parallel splines or lines,
one for each color in the list, in the order given.
The head arrow, if any, is drawn using the first color in the list, and the tail arrow, if any, the second color. This supports the common case of drawing opposing edges, but using parallel splines instead of separately routed multiedges.
If any fraction is used, the colors are drawn in series, with each color being given roughly its specified fraction of the edge.
For example, the graph:
yields:
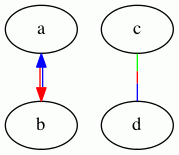
See also:
Valid on:- Clusters
- Edges
- Nodes
colorscheme
type: string, default: ""
This attribute specifies a color scheme namespace: the context for interpreting color names.
In particular, if a color value has form "xxx" or "//xxx",
then the color xxx will be evaluated according to the current color scheme.
If no color scheme is set, the standard X11 naming is used.
For example, if colorscheme=oranges9 (from Brewer color schemes), then color=7 is interpreted as
color="/oranges9/7", the 7th color in the oranges9 colorscheme.
See also:
Valid on:- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
comment
type: string, default: ""
Comments are inserted into output. Device-dependent
Outputs SVG with comments:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd">
<!-- Generated by graphviz version 2.47.1 (20210417.1919)
-->
<!-- This is a graph -->
<!-- Pages: 1 -->
<svg width="62pt" height="116pt"
viewBox="0.00 0.00 62.00 116.00" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink">
<g id="graph0" class="graph" transform="scale(1 1) rotate(0) translate(4 112)">
<polygon fill="white" stroke="transparent" points="-4,4 -4,-112 58,-112 58,4 -4,4"/>
<!-- A -->
<!-- I am node A -->
<g id="node1" class="node">
<title>A</title>
<ellipse fill="none" stroke="black" cx="27" cy="-90" rx="27" ry="18"/>
<text text-anchor="middle" x="27" y="-86.3" font-family="Times,serif" font-size="14.00">A</text>
</g>
<!-- B -->
<!-- I am node B -->
<g id="node2" class="node">
<title>B</title>
<ellipse fill="none" stroke="black" cx="27" cy="-18" rx="27" ry="18"/>
<text text-anchor="middle" x="27" y="-14.3" font-family="Times,serif" font-size="14.00">B</text>
</g>
<!-- A->B -->
<!-- I am an edge -->
<g id="edge1" class="edge">
<title>A->B</title>
<path fill="none" stroke="black" d="M27,-71.7C27,-63.98 27,-54.71 27,-46.11"/>
<polygon fill="black" stroke="black" points="30.5,-46.1 27,-36.1 23.5,-46.1 30.5,-46.1"/>
</g>
</g>
</svg>
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
compound
type: bool, default: false
If true, allow edges between clusters.
Valid on:- Graphs
concentrate
type: bool, default: false
If true, use edge concentrators.
This merges multiedges into a single edge and causes partially parallel
edges to share part of their paths. The latter feature is not yet available
outside of dot.
- Graphs
constraint
type: bool, default: true
If false, the edge is not used in ranking the nodes. For example, in the graph:
the edge b -> c does not add a constraint during rank
assignment, so the only constraints are that a be above b and c,
yielding the graph:
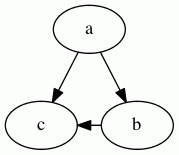
- Edges
Damping
type: double, default: 0.99, minimum: 0.0
Factor damping force motions. On each iteration, a node’s movement
is limited to this factor of its potential motion. By being less than
1.0, the system tends to “cool”, thereby preventing cycling.
- Graphs
decorate
type: bool, default: false
If true, attach edge label to edge by a 2-segment polyline, underlining the label, then going to the closest point of spline.
- Edges
defaultdist
type: double, default: 1+(avg. len)*sqrt(|V|), minimum: epsilon
This specifies the distance between nodes in separate connected components. If set too small, connected components may overlap.
Only applicable if pack=false.
- Graphs
dim
type: int, default: 2, minimum: 2
Set the number of dimensions used for the layout.
The maximum value allowed is 10.
- Graphs
dimen
type: int, default: 2, minimum: 2
Set the number of dimensions used for rendering.
The maximum value allowed is 10.
If both dimen and dim are set, the latter specifies
the dimension used for layout, and the former for rendering.
If only dimen is set, this is used for both layout and rendering
dimensions.
Note that, at present, all aspects of rendering are 2D. This includes
the shape and size of nodes, overlap removal, and edge routing. Thus,
for dimen > 2, the only valid information is the pos
attribute of the nodes.
All other coordinates will be 2D and, at best, will reflect a projection of a higher-dimensional point onto the plane.
Valid on:- Graphs
dir
type: dirType, default: forward (directed) , none (undirected)
Edge type for drawing arrowheads.
Indicates which ends of the edge should be decorated with an arrowhead.
The actual style of the arrowhead can be specified using the
arrowhead and arrowtail attributes.
See limitation.
- Edges
diredgeconstraints
type: string | bool, default: false
If true, constraints are generated for each edge in the largest (heuristic) directed acyclic subgraph such that the edge must point downwards.
Only valid when mode=“ipsep”.
If hier, generates level constraints similar to those used with
mode=“hier”. The main difference is that, in the latter
case, only these constraints are involved, so a faster solver can be used.
- Graphs
distortion
type: double, default: 0.0, minimum: -100.0
Distortion factor for shape=polygon.
Positive values cause top part to be larger than bottom; negative values do the opposite.
See also skew.
- Nodes
dpi
type: double, default: 96.0, 0.0
Specifies the expected number of pixels per inch on a display device.
For bitmap output, dpi guarantees that text rendering will be done more
accurately, both in size and in placement.
For SVG output, dpi guarantees the dimensions in the output correspond to
the correct number of points or inches.
- Graphs
edgehref
type: escString, default: ""
Synonym for edgeURL.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
edgetarget
type: escString, default: <none>
If the edge has a URL or edgeURL
attribute, edgetarget determines which window of the
browser is used
for the URL attached to the non-label part of the edge.
Setting edgetarget=_graphviz will open a new window if it
doesn’t already exist, or reuse it if it does.
If undefined, the value of the target is used instead.
- Edges
edgetooltip
type: escString, default: ""
Tooltip annotation attached to the non-label part of an edge.
Valid on:- Edges
edgeURL
type: escString, default: ""
The link for the non-label parts of an edge.
edgeURL overrides any URL defined for the edge.
Also, edgeURL is used near the head or tail node unless overridden
by headURL or tailURL, respectively.
See limitation.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
epsilon
type: double, default: .0001 * # nodes (mode == KK)' , .0001 (mode == major) , .01 (mode == sgd)
Terminating condition. If the length squared of all energy gradients are
less than epsilon, the algorithm stops.
- Graphs
esep
type: addDouble | addPoint, default: +3
Margin used around polygons for purposes of spline edge routing.
The interpretation is the same as given for sep. esep should
normally be strictly less than sep.
- Graphs
fillcolor
type: color | colorList, default: lightgrey (nodes) , black (clusters)
Color used to fill the background of a node or cluster
assuming style=filled, or a filled arrowhead.
If fillcolor is not defined, color is
used. (For clusters, if color is not defined,
bgcolor is used.) If this is not defined,
the default is used, except for
shape=point or when the output
format is MIF,
which use black by default.
If the value is a colorList, a gradient fill is
used. By default, this is a linear fill; setting style=radial will
cause a radial fill. At present, only two colors are used. If the second
color (after a colon) is missing, the default color is used for it.
See also the gradientangle attribute
for setting the gradient angle.
Note that a cluster inherits the root graph’s attributes if defined.
Thus, if the root graph has defined a fillcolor, this will override a
color or bgcolor attribute set for the cluster.
- Clusters
- Edges
- Nodes
fixedsize
type: bool | string, default: false
If false, the size of a node is determined by smallest width and height
needed to contain its label and image, if any, with a margin specified by
the margin attribute.
The width and height must also be at least as large as the sizes specified by
the width and height attributes, which specify
the minimum values for these parameters.
If true, the node size is specified by the values of the width
and height attributes only and is not expanded to contain the
text label. There will be a warning if the label (with margin) cannot fit
within these limits.
If the fixedsize attribute is set to shape, the
width and height attributes also determine the size
of the node shape, but the label can be much larger. Both the label and shape
sizes are used when avoiding node overlap, but all edges to the node ignore
the label and only contact the node shape. No warning is given if the label
is too large.
- Nodes
fontcolor
type: color, default: black
Color used for text.
Valid on:- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
fontname
type: string, default: "Times-Roman"
Font used for text. This very much depends on the output format and, for non-bitmap output such as PostScript or SVG, the availability of the font when the graph is displayed or printed. As such, it is best to rely on font faces that are generally available, such as Times-Roman, Helvetica or Courier.
How font names are resolved also depends on the underlying library that
handles font name resolution. If Graphviz was built using the fontconfig
library, the
latter library will be used to search for the font. See the commands
fc-list, fc-match and the other fontconfig commands for how names are
resolved and which fonts are available. Other systems may provide their own
font package, such as Quartz for OS X.
Note that various font attributes, such as weight and slant, can be built
into the font name. Unfortunately, the syntax varies depending on which font
system is dominant. Thus, using fontname="times bold italic" will produce a
bold, slanted Times font using Pango, the usual main font library.
Alternatively, fontname="times:italic" will produce a slanted Times font from
fontconfig, while fontname="times-bold" will resolve to a bold Times using
Quartz. You will need to ascertain which package is used by your Graphviz
system and refer to the relevant documentation.
If Graphviz is not built with a high-level font library, fontname will be
considered the name of a Type 1 or True Type font file. If you specify
fontname=schlbk, the tool will look for a file named schlbk.ttf or schlbk.pfa
or schlbk.pfb in one of the directories specified by the
fontpath attribute. The lookup does support various aliases
for the common fonts.
- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
fontnames
type: string, default: ""
Allows user control of how basic fontnames are represented in SVG output.
If fontnames is undefined or svg, the output will try to use known SVG
fontnames.
For example, the default font Times-Roman will be mapped to the
basic SVG font serif. This can be overridden by setting fontnames to ps
or hd. In the former case, known PostScript font names such as
Times-Roman will be used in the output. In the latter case, the fontconfig
font conventions are used. Thus, Times-Roman would be treated as Nimbus Roman No9 L. These last two options are useful with SVG viewers that support
these richer fontname spaces.
- Graphs
fontpath
type: string, default: <system-dependent>
Directory list used by libgd to search for bitmap fonts if Graphviz was not built with the fontconfig library.
If fontpath is not set, the environment
variable DOTFONTPATH is checked.
If DOTFONTPATH is not set, GDFONTPATH is checked.
If GDFONTPATH not set, libgd uses its compiled-in font path.
Note that fontpath is an attribute of the root graph.
- Graphs
fontsize
type: double, default: 14.0, minimum: 1.0
Font size, in points, used for text.
Valid on:- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
forcelabels
type: bool, default: true
If true, all xlabel attributes are placed, even if there is some overlap with nodes or other labels.
- Graphs
gradientangle
type: int, default: ""
If a gradient fill is being used, this determines the angle of the fill.
For linear fills, the colors transform along a line specified by the angle and the center of the object. For radial fills, a value of zero causes the colors to transform radially from the center; for non-zero values, the colors transform from a point near the object’s periphery as specified by the value.
If unset, the default angle is 0.
Valid on:- Clusters
- Graphs
- Nodes
group
type: string, default: ""
If the end points of an edge belong to the same group, i.e., have the
same group attribute, parameters are set to avoid crossings and keep
the edges straight.
- Nodes
head_lp
type: point
Position of an edge’s head label, in points. The position indicates the center of the label.
Valid on:- Edges
headclip
type: bool, default: true
If true, the head of an edge is clipped to the boundary of the head node; otherwise, the end of the edge goes to the center of the node, or the center of a port, if applicable.
Valid on:- Edges
headhref
type: escString, default: ""
Synonym for headURL.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
headlabel
type: lblString, default: ""
Text label to be placed near head of edge.
See limitation.
Valid on:- Edges
headport
type: portPos, default: center
Indicates where on the head node to attach the head of the edge. In the default case, the edge is aimed towards the center of the node, and then clipped at the node boundary.
See limitation.
Valid on:- Edges
headtarget
type: escString, default: <none>
If the edge has a headURL,
headtarget determines which window of the
browser is used
for the URL. Setting headURL=_graphviz will open a new window if the window
doesn’t already exist, or reuse the window if it does.
If undefined, the value of the target is used.
- Edges
headtooltip
type: escString, default: ""
Tooltip annotation attached to the head of an edge.
Used only if the edge has a headURL attribute.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
headURL
type: escString, default: ""
If defined, headURL is output as part of the head label of the edge.
Also, this value is used near the head node, overriding any URL value.
See limitation.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
height
type: double, default: 0.5, minimum: 0.02
Height of node, in inches.
This is taken as the initial, minimum height of the node. If
fixedsize is true, this will be the final height of the
node. Otherwise, if the node label requires more height to fit, the node’s height
will be increased to contain the label.
If the output format is dot, the value given to height will be the final
value.
If the node shape is regular, the width and height are made identical:
- If both the
widthand theheightare set explicitly, the maximum of the two values is used. - If one of
widthorheightis set explicitly, that value is used for bothwidthandheight. - If neither is set explicitly, the minimum of the two default values is used.
See also:
Valid on:- Nodes
href
type: escString, default: ""
Synonym for URL.
See also:
Valid on:- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
id
type: escString, default: ""
Allows the graph author to provide an identifier for graph objects which is to be included in the output.
Normal \N, \E, \G substitutions are applied.
If provided, it is the responsibility of the provider to keep
id values unique for its intended downstream use.
Note, in particular, that \E does not provide a unique id for multi-edges.
If no id attribute is provided, then a unique internal id is used. However,
this value is unpredictable by the graph writer.
If the graph provides an id attribute, this will be used as a prefix for
internally generated attributes. By making internally-used attributes
distinct, the user can include multiple image maps in the same document.
- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
image
type: string, default: ""
Gives the name of a file containing an image to be displayed inside a node. The image file must be in one of the recognized formats, typically JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, SVG, or Postscript, and be able to be converted into the desired output format.
The file must contain the image size information:
- Bitmap formats usually already contain image size.
- PostScript files must contain a line starting with
%%BoundingBox:followed by four integers specifying the lower left x and y coordinates and the upper right x and y coordinates of the bounding box for the image, the coordinates being in points. - An SVG image file must contain width and height attributes, typically as part
of the svg element. The values for these should have the form of a floating
point number, followed by optional units, e.g.,
width="76pt". Recognized units are in, px, pc, pt, cm and mm for inches, pixels, picas, points, centimeters and millimeters, respectively. The default unit is points.
Unlike with the shapefile attribute, the image is treated
as node content rather than the entire node. In particular, an image can be
contained in a node of any shape, not just a rectangle.
- Nodes
imagepath
type: string, default: ""
Specifies a list of directories in which to look for image files as specified
by the image attribute or using the IMG element in HTML-like
labels.
imagepath should be a list of (absolute or
relative) pathnames, each separated by a semicolon ; (for Windows) or a colon :
(all other OS).
The first directory in which a file of the given name is found will be used to load the image.
If imagepath is not set, relative pathnames for the image file will be
interpreted with respect to the current working directory.
- Graphs
imagepos
type: string, default: "mc"
Controls how an image is positioned within its containing node.
imagepos only has an effect when the image is smaller than the containing node.
The default is to be centered both horizontally and vertically.
Valid values:
tl- Top Lefttc- Top Centeredtr- Top Rightml- Middle Leftmc- Middle Centered (the default)mr- Middle Rightbl- Bottom Leftbc- Bottom Centeredbr- Bottom Right
- Nodes
imagescale
type: bool | string, default: false
Controls how an image fills its containing node.
In general, the image is given its natural size,
(cf. dpi),
and the node size is made large enough to contain its image, its
label, its margin, and its peripheries.
Its width and height will also be at least as large as its
minimum width and height.
If, however, fixedsize=true,
the width and height attributes specify the exact size of the node.
- During rendering, in the default case (
imagescale=false), the image retains its natural size. - If
imagescale=true, the image is uniformly scaled (i.e., its aspect ratio is preserved) to fit inside the node. At least one dimension of the image will be as large as possible given the size of the node. - When
imagescale=width, the width of the image is scaled to fill the node width. - The corresponding property holds when
imagescale=height. - When
imagescale=both, both the height and the width are scaled separately to fill the node.
In all cases, if a dimension of the image is larger than the corresponding dimension of the node, that dimension of the image is scaled down to fit the node.
As with the case of expansion, if imagescale=true, width and height are
scaled uniformly.
- Nodes
inputscale
type: double, default: <none>
For layout algorithms that support initial input positions (specified by the pos attribute),
this attribute can be used to appropriately scale the values.
By default, fdp and neato interpret
the x and y values of pos as being in inches. (NOTE: neato -n(2) treats the coordinates as
being in points, being the unit used by the layout algorithms for the pos attribute.) Thus, if
the graph has pos attributes in points, one should set inputscale=72.
This can also be set on the command line using the -s flag.
If unset, no scaling is done and the units on input are treated as inches.
inputscale=0 is equivalent to inputscale=72.
- Graphs
K
type: double, default: 0.3, minimum: 0
Spring constant used in virtual physical model. It roughly corresponds
to an ideal edge length (in inches), in that increasing K tends to
increase the distance between nodes.
Note that the edge attribute len can be used to
override this value for adjacent nodes.
- Clusters
- Graphs
label
type: lblString, default: "\N" (nodes) , "" (otherwise)
Text label attached to objects.
If a node’s shape is record, then the label can
have a special format
which describes the record layout.
Note that a node’s default label is "\N", so the node’s name or ID becomes
its label.
Technically, a node’s name can be an HTML string but this will not mean that the node’s label will be interpreted as an HTML-like label. This is because the node’s actual label is an ordinary string, which will be replaced by the raw bytes stored in the node’s name.
To get an HTML-like label, the label attribute value itself must be an HTML string.
- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
label_scheme
type: int, default: 0, minimum: 0
Whether to treat a node whose name has the form |edgelabel|* as a special node representing an edge label.
- The default,
label_scheme=0, produces no effect. - If
label_scheme=1,sfdpuses a penalty-based method to make that kind of node close to the center of its neighbor. - With
label_scheme=2,sfdpuses a penalty-based method to make that kind of node close to the old center of its neighbor. - Finally,
label_scheme=3invokes a two-step process of overlap removal and straightening.
- Graphs
labelangle
type: double, default: -25.0, minimum: -180.0
Determines, along with labeldistance,
where the headlabel / taillabel are
placed with respect to the head / tail in polar coordinates.
The origin in the coordinate system is the point where the edge touches the node. The ray of 0 degrees goes from the origin back along the edge, parallel to the edge at the origin.
The angle, in degrees, specifies the rotation from the 0 degree ray, with positive angles moving counterclockwise and negative angles moving clockwise.
Valid on:- Edges
labeldistance
type: double, default: 1.0, minimum: 0.0
Multiplicative scaling factor adjusting the distance that the
headlabel / taillabel is from the head /
tail node.
The default distance is 10 points.
See labelangle for more details.
- Edges
labelfloat
type: bool, default: false
If true, allows edge labels to be less constrained in position. In particular, it may appear on top of other edges.
Valid on:- Edges
labelfontcolor
type: color, default: black
Color used for headlabel and taillabel.
If not set, defaults to edge’s fontcolor.
- Edges
labelfontname
type: string, default: "Times-Roman"
Font used for headlabel and taillabel.
If not set, defaults to edge’s fontname.
- Edges
labelfontsize
type: double, default: 14.0, minimum: 1.0
Font size, in points, used for headlabel and
taillabel.
If not set, defaults to edge’s fontsize.
- Edges
labelhref
type: escString, default: ""
Synonym for labelURL.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
labeljust
type: string, default: "c"
Justification for graph & cluster labels.
- If
labeljust=r, the label is right-justified within bounding rectangle - If
labeljust=l, left-justified - Else the label is centered.
Note that a subgraph inherits attributes from its parent. Thus, if
the root graph sets labeljust=l, the subgraph inherits
this value.
- Clusters
- Graphs
labelloc
type: string, default: "t" (clusters) , "b" (root graphs) , "c" (nodes)
Vertical placement of labels for nodes, root graphs and clusters.
For graphs and clusters, only labelloc=t and labelloc=b are allowed, corresponding
to placement at the top and bottom, respectively.
By default, root graph labels go on the bottom and cluster labels go on the top.
Note that a subgraph inherits attributes from its parent. Thus, if
the root graph sets labelloc=b, the subgraph inherits
this value.
For nodes, this attribute is used only when the height of the node is larger than the height of its label.
If labelloc=t, labelloc=c, labelloc=b, the label is aligned
with the top, centered, or aligned with the bottom of the node, respectively.
By default, the label is vertically centered.
- Clusters
- Graphs
- Nodes
labeltarget
type: escString, default: <none>
If the edge has a URL or labelURL attribute, this
attribute determines which window of the browser is used for the URL attached
to the label.
Setting labeltarget=_graphviz will open a new window if it doesn’t
already exist, or reuse it if it does.
If undefined, the value of the target is used.
- Edges
labeltooltip
type: escString, default: ""
Tooltip annotation attached to label of an edge.
Valid on:- Edges
labelURL
type: escString, default: ""
If defined, labelURL is the link used for the label of an edge.
labelURL overrides any URL defined for the edge.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
landscape
type: bool, default: false
If true, the graph is rendered in landscape mode. Synonymous with
rotate=90 or orientation=landscape.
See also:
Valid on:- Graphs
layer
type: layerRange, default: ""
Specifies layers in which the node, edge or cluster is present.
Valid on:- Clusters
- Edges
- Nodes
layerlistsep
type: string, default: ","
Specifies the separator characters used to split an attribute of type
layerRange into a list of ranges.
- Graphs
layers
type: layerList, default: ""
Specifies a linearly ordered list of layer names attached to the graph
The graph is then output in separate layers. Only those components belonging to the current output layer appear.
See How to use drawing layers (overlays).
Valid on:- Graphs
layerselect
type: layerRange, default: ""
Selects a list of layers to be emitted.
Valid on:- Graphs
layersep
type: string, default: ":\t "
Specifies the separator characters used to split the layers attribute into a list of layer names.
- Graphs
layout
type: string, default: ""
Specifies the name of the layout algorithm to use, such as dot or neato.
Normally, graphs should be kept independent of a type of layout. In some cases, however, it can be convenient to embed the type of layout desired within the graph.
For example, a graph containing position information from a layout might want to record what the associated layout algorithm was.
This attribute takes precedence over the -K flag or
the actual command name used.
- Graphs
len
type: double, default: 1.0 (neato) , 0.3 (fdp)
Preferred edge length, in inches.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
levels
type: int, default: MAXINT, minimum: 0.0
Number of levels allowed in the multilevel scheme.
Valid on:- Graphs
levelsgap
type: double, default: 0.0
Specifies strictness of level constraints in neato when
mode=“ipsep” or mode=hier.
Larger positive values mean stricter constraints, which demand more separation between levels. On the other hand, negative values will relax the constraints by allowing some overlap between the levels.
Valid on:- Graphs
lhead
type: string, default: ""
Logical head of an edge.
When compound is true, if lhead is defined and is the name
of a cluster containing the real head, the edge is clipped to the boundary of
the cluster.
See limitation.
Valid on:- Edges
lheight
type: double
Height of graph or cluster label, in inches.
Valid on:- Clusters
- Graphs
lp
type: point
Label position, in points.
The position indicates the center of the label.
Valid on:- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
ltail
type: string, default: ""
Logical tail of an edge.
When compound=true, if ltail is defined and is the name
of a cluster containing the real tail, the edge is clipped to the boundary of
the cluster.
See limitation.
Valid on:- Edges
lwidth
type: double
Width of graph or cluster label, in inches.
Valid on:- Clusters
- Graphs
margin
type: double | point, default: <device-dependent>
For graphs, this sets x and y margins of canvas, in inches.
If the margin is a single double, both margins are set equal to the given value.
Note that the margin is not part of the drawing but just empty space left
around the drawing. The margin basically corresponds to a translation of
drawing, as would be necessary to center a drawing on a page. Nothing is
actually drawn in the margin. To actually extend the background of a drawing,
see the pad attribute.
For clusters, margin specifies the space between the nodes in the cluster
and the cluster bounding box. By default, this is 8 points.
For nodes, this attribute specifies space left around the node’s label. By
default, the value is 0.11,0.055.
- Clusters
- Graphs
- Nodes
maxiter
type: int, default: 100 * # nodes (mode == KK) , 200 (mode == major) , 30 (mode == sgd) , 600 (fdp)
Sets the number of iterations used.
Valid on:- Graphs
mclimit
type: double, default: 1.0
Multiplicative scale factor used to alter the MinQuit (default = 8)
and MaxIter (default = 24) parameters used during crossing
minimization.
These correspond to the number of tries without improvement before quitting and the maximum number of iterations in each pass.
Valid on:- Graphs
mindist
type: double, default: 1.0, minimum: 0.0
Specifies the minimum separation between all nodes.
Valid on:- Graphs
minlen
type: int, default: 1, minimum: 0
Minimum edge length (rank difference between head and tail).
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
mode
type: string, default: major
Technique for optimizing the layout.
- For neato, if
mode="major",neatouses stress majorization. - If
mode="KK",neatouses a version of the gradient descent method.KKis sometimes appreciably faster for small (number of nodes < 100) graphs. A significant disadvantage is thatKKmay cycle. - If
mode="sgd",neatouses a version of the stochastic gradient descent method.sgd’s advantage is faster and more reliable convergence than both the previous methods, whilesgd’s disadvantage is that it runs in a fixed number of iterations and may require larger values ofmaxiterin some graphs.
There are two experimental modes in neato:
mode="hier", which adds a top-down directionality similar to the layout used indot, andmode="ipsep", which allows the graph to specify minimum vertical and horizontal distances between nodes. (See the sep attribute.)
For sfdp, the default is mode="spring", which corresponds to using a
spring-electrical model. Setting mode="maxent" causes a similar model
to be run but one that also takes into account edge lengths specified by the
len attribute.
- Graphs
model
type: string, default: shortpath
Specifies how the distance matrix is computed for the input graph.
The distance matrix specifies the ideal distance between every pair of nodes.
neato attemps to find a layout which best achieves these distances. By
default, it uses the length of the shortest path, where the length of each
edge is given by its len attribute.
- If
model="circuit", neato uses the circuit resistance model to compute the distances. This tends to emphasize clusters. - If
model="subset", neato uses the subset model. This sets the edge length to be the number of nodes that are neighbors of exactly one of the end points, and then calculates the shortest paths. This helps to separate nodes with high degree.
For more control of distances, one can use model=mds. In this case, the
len of an edge is used as the ideal distance between its vertices.
A shortest path calculation is only used for pairs of nodes not connected by an edge. Thus, by supplying a complete graph, the input can specify all of the relevant distances.
Valid on:- Graphs
mosek
type: bool, default: false
If Graphviz is built with MOSEK defined, mode=ipsep and mosek=true,
the Mosek software is use to solve the ipsep constraints.
- Graphs
newrank
type: bool, default: false
Whether to use a single global ranking, ignoring clusters.
The original ranking algorithm in dot is recursive on clusters. This can
produce fewer ranks and a more compact layout, but sometimes at the cost of a
head node being place on a higher rank than the tail node. It also assumes
that a node is not constrained in separate, incompatible subgraphs. For
example, a node cannot be in a cluster and also be constrained by rank=same
with a node not in the cluster.
This allows nodes to be subject to multiple constraints. Rank constraints will usually take precedence over edge constraints.
Valid on:- Graphs
nodesep
type: double, default: 0.25, minimum: 0.02
In dot, nodesep specifies the minimum space between two adjacent nodes in the same rank, in inches.
For other layouts, nodesep affects the spacing between loops on a single node, or multiedges between
a pair of nodes.
- Graphs
nojustify
type: bool, default: false
By default, the justification of multi-line labels is done within the largest
context that makes sense. Thus, in the label of a polygonal node, a
left-justified line will align with the left side of the node (shifted by the
prescribed margin). In record nodes, left-justified line will
line up with the left side of the enclosing column of fields. If
nojustify=true, multi-line labels will be justified in the context
of itself.
For example, if nojustify is set, the first label line is long, and the
second is shorter and left-justified, the second will align with the
left-most character in the first line, regardless of how large the node might
be.
- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
normalize
type: double | bool, default: false
Normalizes coordinates of final layout so that the first point is at the
origin, and then rotates the layout so that the angle of the first edge is
specified by the value of normalize in degrees.
If normalize is not a number, it is evaluated as a bool, with true
corresponding to 0 degrees.
NOTE: Since the attribute is evaluated first as a number, 0 and 1
cannot be used for false and true.
- Graphs
notranslate
type: bool, default: false
By default, the final layout is translated so that the lower-left corner of the bounding box is at the origin.
This can be annoying if some nodes are pinned or if the user runs neato -n.
To avoid this translation, set notranslate=true.
- Graphs
nslimit
type: double
Sets number of iterations in network simplex applications.
nslimit is used in computing node x coordinates.
If defined, # iterations = nslimit * # nodes; otherwise, # iterations = MAXINT.
- Graphs
nslimit1
type: double
Sets number of iterations in network simplex applications.
nslimit1 is used for ranking nodes.
If defined, # iterations = nslimit * # nodes; otherwise, # iterations = MAXINT.
- Graphs
ordering
type: string, default: ""
If ordering="out", then the outedges of a node, that is, edges with the
node as its tail node, must appear left-to-right in the same order in which
they are defined in the input.
If ordering="in", then the inedges of a node must appear
left-to-right in the same order in which they are defined in the input.
If defined as a graph or subgraph attribute, the value is applied to all nodes in the graph or subgraph.
Note that the graph attribute takes precedence over the node attribute.
Valid on:- Graphs
- Nodes
orientation
type: double | string, default: 0.0, "", minimum: 360.0
When used on nodes: Angle, in degrees, to rotate polygon node shapes. For any number of polygon sides, 0 degrees rotation results in a flat base.
When used on graphs: If "[lL]*", sets graph orientation to landscape.
Used only if rotate is not defined.
See also:
Valid on:- Graphs
- Nodes
outputorder
type: outputMode, default: breadthfirst
Specify order in which nodes and edges are drawn.
Valid on:- Graphs
overlap
type: string | bool, default: true
Determines if and how node overlaps should be removed.
Nodes are first
enlarged using the sep attribute. If true , overlaps are
retained. If the value is "scale", overlaps are removed by uniformly scaling
in x and y. If the value converts to "false", and it is available, Prism, a
proximity graph-based algorithm, is used to remove node overlaps. This can
also be invoked explicitly with overlap=prism. This technique starts with a
small scaling up, controlled by the overlap_scaling
attribute, which can remove a significant portion of the overlap. The prism
option also accepts an optional non-negative integer suffix. This can be used
to control the number of attempts made at overlap removal. By default,
overlap="prism" is equivalent to overlap="prism1000". Setting
overlap="prism0" causes only the scaling phase to be run.
If Prism is not available, or the version of Graphviz is earlier than 2.28,
"overlap=false" uses a Voronoi-based technique. This can always be invoked
explicitly with "overlap=voronoi".
If overlap="scalexy", x and y are separately scaled to remove overlaps.
If overlay="compress", the layout will be scaled down as much as
possible without introducing any overlaps, obviously assuming there are none
to begin with.
**N.B.**The remaining allowed values of overlap correspond to algorithms which, at present, can produce bad aspect ratios. In addition, we deprecate the use of the "ortho*" and "portho*".
If the value is "vpsc", overlap removal is done as a quadratic optimization
to minimize node displacement while removing node overlaps.
If the value is "orthoxy" or "orthoyx", overlaps are moved by optimizing two
constraint problems, one for the x axis and one for the y. The suffix
indicates which axis is processed first. If the value is “ortho”, the
technique is similar to “orthoxy” except a heuristic is used to reduce the
bias between the two passes. If the value is "ortho_yx", the technique is
the same as "ortho", except the roles of x and y are reversed. The values
"portho", "porthoxy", "porthoxy", and "portho_yx" are similar to the
previous four, except only pseudo-orthogonal ordering is enforced.
If the layout is done by neato with mode=“ipsep”, then one can use
overlap=ipsep. In this case, the overlap removal constraints are
incorporated into the layout algorithm itself. N.B. At present, this only
supports one level of clustering.
Except for fdp and sfdp, the layouts assume overlap="true" as the default.
Fdp first uses a number of passes using a built-in, force-directed technique
to try to remove overlaps. Thus, fdp accepts overlap with an integer
prefix followed by a colon, specifying the number of tries. If there is no
prefix, no initial tries will be performed. If there is nothing following a
colon, none of the above methods will be attempted. By default, fdp uses
overlap="9:prism". Note that overlap="true", overlap="0:true" and
overlap="0:" all turn off all overlap removal.
By default, sfdp uses overlap="prism0".
Except for the Voronoi and prism methods, all of these transforms preserve
the orthogonal ordering of the original layout. That is, if the x coordinates
of two nodes are originally the same, they will remain the same, and if the x
coordinate of one node is originally less than the x coordinate of another,
this relation will still hold in the transformed layout. The similar
properties hold for the y coordinates. This is not quite true for the
"porth*" cases. For these, orthogonal ordering is only preserved among nodes
related by an edge.
- Graphs
overlap_scaling
type: double, default: -4, minimum: -10000000000
When overlap=prism, the layout is scaled by this factor, thereby
removing a fair amount of node overlap, and making node overlap removal
faster and better able to retain the graph’s shape.
-
If
overlap_scalingis negative, the layout is scaled by-1*overlap_scalingtimes the average label size. -
If
overlap_scalingis positive, the layout is scaled byoverlap_scaling. -
If
overlap_scalingis zero, no scaling is done.
- Graphs
overlap_shrink
type: bool, default: true
Whether the overlap removal algorithm should perform a compression pass to reduce the size of the layout.
Valid on:- Graphs
pack
type: bool | int, default: false
Whether each connected component of the graph should be laid out separately, and then the graphs packed together.
If pack has an integral value, this is used as the size,
in points,of a margin around each part; otherwise, a default
margin of 8 is used.
If pack is interpreted as false, the entire graph is laid out together.
The granularity and method of packing is influenced by the
packmode attribute.
For layouts which always do packing, such as twopi, the pack
attribute is just used to set the margin.
pack is treated as true if the value of pack is true (case-insensitive)
or a non-negative integer.
- Graphs
packmode
type: packMode, default: node
This indicates how connected components should be packed (cf.
packMode). Note that defining packmode will automatically
turn on packing as though one had set pack=true.
- Graphs
pad
type: double | point, default: 0.0555 (4 points)
Specifies how much, in inches, to extend the drawing area around the minimal area needed to draw the graph.
If pad is a single double, both the x and y pad values are set
equal to the given value. This area is part of the
drawing and will be filled with the background color, if appropriate.
Normally, a small pad is used for aesthetic reasons, especially when
a background color is used, to avoid having nodes and edges abutting
the boundary of the drawn region.
- Graphs
page
Width and height of output pages, in inches.
If only a single value is given, this is used for both the width and height.
If page is set and is smaller than the size of the layout, a rectangular
array of pages of the specified page size is overlaid on the layout, with
origins aligned in the lower-left corner, thereby partitioning the layout
into pages. The pages are then produced one at a time, in
pagedir order.
At present, page only works for PostScript output. For other types of output,
use another tool to split the output into multiple output files,
or use viewport to generate multiple files.
- Graphs
pagedir
type: pagedir, default: BL
The order in which pages are emitted.
Used only if page is set and applicable.
Limited to one of the 8 row or column major orders.
Valid on:- Graphs
pencolor
type: color, default: black
Color used to draw the bounding box around a cluster.
If pencolor is not defined, color is used.
If color is not defined, bgcolor is used.
If bgcolor is not defined, the default is used.
Note that a cluster inherits the root graph’s attributes if defined. Thus, if
the root graph has defined a pencolor, this will override a color or
bgcolor attribute set for the cluster.
- Clusters
penwidth
type: double, default: 1.0, minimum: 0.0
Specifies the width of the pen, in points, used to draw lines and curves, including the boundaries of edges and clusters.
penwidth value is inherited by subclusters, and has no effect on text.
Previous to 31 January 2008, the effect of penwidth=W was achieved by
including setlinewidth(W) as part of a style specification.
If both attributes are set, penwidth will be used.
- Clusters
- Edges
- Nodes
peripheries
type: int, default: <shape default> (nodes) , 1 (clusters) , minimum: 0
Set number of peripheries used in polygonal shapes and cluster boundaries.
Note that user-defined shapes are treated as a form of
box shape, so the default peripheries value is 1 and the user-defined shape
will be drawn in a bounding rectangle. Setting peripheries=0 will turn this
off.
peripheries=1 is the maximum value for clusters.
- Clusters
- Nodes
pin
type: bool, default: false
Keeps the node at the node’s given input position.
If true and the node has a pos attribute on input, neato or
fdp prevents the node from moving from the input position. This property
can also be specified in the pos attribute itself (cf. the point
type).
Note: Due to an artifact of the implementation, previous to 27 Feb 2014, final coordinates are translated to the origin. Thus, if you look at the output coordinates given in the (x)dot or plain format, pinned nodes will not have the same output coordinates as were given on input. If this is important, a simple workaround is to maintain the coordinates of a pinned node. The vector difference between the old and new coordinates will give the translation, which can then be subtracted from all of the appropriate coordinates.
After 27 Feb 2014, this translation can be avoided in neato by setting
notranslate=true. However, if the graph specifies node
overlap removal or a change in aspect ratio, node
coordinates may still change.
- Nodes
pos
type: point | splineType
Position of node, or spline control points.
For nodes, the position indicates the center of the node. On output, the coordinates are in points.
In neato and fdp, pos can be used to set the initial position of a
node. By default, the coordinates are assumed to be in inches. However, the
-s command line flag can be used to specify different
units. As the output coordinates are in points, feeding the output of a graph
laid out by a Graphviz program into neato or fdp will almost always
require the -s flag.
When the -n command line flag is used with neato, it
is assumed the positions have been set by one of the layout programs, and are
therefore in points. Thus, neato -n can accept input correctly without
requiring a -s flag and, in fact, ignores any such flag.
- Edges
- Nodes
quadtree
type: quadType | bool, default: normal
Quadtree scheme to use.
quadtree=truealiasesquadtree=normalquadtree=falsealiasesquadtree=nonequadtree=2aliasesquadtree=fast
- Graphs
quantum
type: double, default: 0.0, minimum: 0.0
If quantum > 0.0, node label dimensions will be rounded to integral multiples of the quantum.
- Graphs
rank
type: rankType
Rank constraints on the nodes in a subgraph.
- If
rank="same", all nodes are placed on the same rank. - If
rank="min", all nodes are placed on the minimum rank. - If
rank="source", all nodes are placed on the minimum rank, and the only nodes on the minimum rank belong to some subgraph withrank="source"orrank="min".
Analogous criteria hold for rank="max" and rank="sink".
(Note: the minimum rank is topmost or leftmost, and the maximum rank is bottommost or rightmost.)
Valid on:- Subgraphs
rankdir
type: rankdir, default: TB
Sets direction of graph layout.
For example, if rankdir="LR", and barring cycles, an edge T -> H; will go
from left to right. By default, graphs are laid out from top to bottom.
This attribute also has a side-effect in determining how record nodes are interpreted. See record shapes.
Valid on:- Graphs
ranksep
type: double | doubleList, default: 0.5 (dot) , 1.0 (twopi) , minimum: 0.02
In dot, sets the desired rank separation, in inches.
This is the minimum vertical distance between the bottom of the nodes in one
rank and the tops of nodes in the next. If the value contains equally, the
centers of all ranks are spaced equally apart. Note that both
settings are possible, e.g., ranksep="1.2 equally".
In twopi, this attribute specifies the radial separation of concentric circles.
For twopi, ranksep can also be a list of doubles. The first double specifies
the radius of the inner circle; the second double specifies the increase in
radius from the first circle to the second; etc. If there are more circles than
numbers, the last number is used as the increment for the remainder.
- Graphs
ratio
Sets the aspect ratio (drawing height/drawing width) for the drawing.
Note that this is adjusted before the size attribute constraints
are enforced.
In addition, the calculations usually ignore the node sizes, so the final drawing size may only approximate what is desired.
If ratio is numeric, ratio is taken as the desired aspect ratio.
Then, if the actual aspect ratio is less than the desired ratio,
the drawing height is scaled up to achieve the
desired ratio; if the actual ratio is greater than that desired ratio,
the drawing width is scaled up.
If ratio="fill" and the size
attribute is set, node positions are scaled, separately in both x
and y, so that the final drawing exactly fills the specified size.
If both size values exceed the width
and height of the drawing, then both coordinate values of each
node are scaled up accordingly. However, if either size dimension
is smaller than the corresponding dimension in the drawing, one
dimension is scaled up so that the final drawing has the same aspect
ratio as specified by size.
Then, when rendered, the layout will be
scaled down uniformly in both dimensions to fit the given
size, which may cause nodes and text
to shrink as well. This may not be what the user
wants, but it avoids the hard problem of how to reposition the
nodes in an acceptable fashion to reduce the drawing size.
If ratio="compress" and the size
attribute is set, dot attempts to compress the initial layout to fit
in the given size. This achieves a tighter packing of nodes but
reduces the balance and symmetry. This feature only works in dot.
If ratio="expand", the size attribute is set, and both the
width and the height of the graph are less than the value in
size, node positions are scaled uniformly until at least one
dimension fits size exactly. Note that this is distinct from
using size as the desired size, as here the drawing is expanded
before edges are generated and all node and text sizes remain unchanged.
If ratio="auto", the page attribute is set and the graph
cannot be drawn on a single page, then size is set to an
“ideal” value.
In particular, the size in a given dimension will be the smallest integral
multiple of the page size in that dimension which is at least half the
current size. The two dimensions are then scaled independently to the
new size. This feature only works in dot.
- Graphs
rects
type: rect
Rectangles for fields of records, in points.
Valid on:- Nodes
regular
type: bool, default: false
If true, force polygon to be regular, i.e., the vertices of the polygon will lie on a circle whose center is the center of the node.
Valid on:- Nodes
remincross
type: bool, default: true
If true and there are multiple clusters, run crossing minimization a second time.
Valid on:- Graphs
repulsiveforce
type: double, default: 1.0, minimum: 0.0
The power of the repulsive force used in an extended Fruchterman-Reingold
force directed model. Values larger than 1 tend to reduce
the warping effect at the expense of less clustering.
- Graphs
resolution
type: double, default: 96.0, 0.0
Synonym for dpi.
- Graphs
root
type: string | bool, default: <none> (graphs) , false (nodes)
Specifies nodes to be used as the center of the layout and the root of the generated spanning tree.
- As a graph attribute, this gives the name of the node.
- As a node attribute, it specifies that the node should be used as a central node.
In twopi, root will actually be the central node. In circo, the
block containing the node will be central in the drawing of its connected
component. If not defined, twopi will pick a most central node, and circo
will pick a random node.
If the root attribute is defined as the empty string, twopi will reset it to
name of the node picked as the root node.
For twopi, it is possible to have multiple roots, presumably one for each
component. If more than one node in a component is marked as the root,
twopi will pick one.
- Graphs
- Nodes
rotate
type: int, default: 0
If rotate=90, sets drawing orientation to landscape.
See also:
Valid on:- Graphs
rotation
type: double, default: 0
Rotates the final layout counter-clockwise by the specified number of degrees.
Valid on:- Graphs
samehead
type: string, default: ""
Edges with the same head and the same samehead value are aimed at the same point on the head.
This has no effect on loops.
Each node can have at most 5 unique samehead values.
See limitation.
See also sametail.
- Edges
sametail
type: string, default: ""
Edges with the same tail and the same sametail value are aimed at the
same point on the tail.
This has no effect on loops.
Each node can have at most 5 unique sametail values.
See limitation.
See also samehead.
- Edges
samplepoints
type: int, default: 8 (output) , 20 (overlap and image maps)
Gives the number of points used for a circle/ellipse node.
Used if the input graph defines the vertices attribute, and
output is dot or xdot.
It plays the same role in neato, when adjusting the layout to avoid
overlapping nodes, and in image maps.
- Nodes
scale
Scales layout by the given factor after the initial layout.
If only a single number is given, that number scales both width and height.
Valid on:- Graphs
searchsize
type: int, default: 30
During network simplex, the maximum number of edges with negative cut values to search when looking for one with minimum cut value.
Valid on:- Graphs
sep
type: addDouble | addPoint, default: +4
Margin to leave around nodes when removing node overlap.
This guarantees a minimal non-zero distance between nodes.
If the attribute begins with a plus sign '+', an additive margin is
specified. That is, "+w,h" causes the node’s bounding box to be increased by
w points on the left and right sides, and by h points on the top and bottom.
Without a plus sign, the node is scaled by 1 + w in the x coordinate and
1 + h in the y coordinate.
If only a single number is given, this is used for both dimensions.
If unset but esep is defined, the sep values will be set to the
esep values divided by 0.8. If esep is unset, the
default value is used.
- Graphs
shape
type: shape, default: ellipse
Sets the shape of a node.
Valid on:- Nodes
shapefile
type: string, default: ""
(Deprecated) Specifies a file containing user-supplied node content.
Sets the node’s shape=“box”. The image in the shapefile must be
rectangular. The image formats supported as well as the precise semantics of
how the file is used depends on the output format. For further
details, see Image Formats and External
PostScript files.
There is one exception to this usage: If shape=“epsf”,
shapefile gives a filename containing a definition of the node in
PostScript. The graphics defined must be contain all of the node content,
including any desired boundaries. For further details, see External
PostScript files.
- Nodes
showboxes
type: int, default: 0, minimum: 0
Print guide boxes in PostScript at the beginning of
routesplines if showboxes=1, or at the end if showboxes=2. (Debugging, TB mode only!)
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
sides
type: int, default: 4, minimum: 0
Number of sides when shape=polygon.
- Nodes
size
Maximum width and height of drawing, in inches.
If only a single number is given, this is used for both the width and the height.
If defined and the drawing is larger than the given size, the drawing is uniformly scaled down so that it fits within the given size.
If size ends in an exclamation point "!", then size is taken to be the
desired minimum size. In this case, if both dimensions of the drawing are
less than size, the drawing is scaled up uniformly until at least one
dimension equals its dimension in size.
There is some interaction between the size and ratio
attributes.
- Graphs
skew
type: double, default: 0.0, minimum: -100.0
Skew factor for shape=polygon.
Positive values skew top of polygon to right; negative to left.
See also distortion.
- Nodes
smoothing
type: smoothType, default: "none"
Specifies a post-processing step used to smooth out an uneven distribution of nodes.
Valid on:- Graphs
sortv
type: int, default: 0, minimum: 0
If packmode indicates an array packing, sortv specifies an
insertion order among the components, with smaller values inserted first.
- Clusters
- Graphs
- Nodes
splines
Controls how, and if, edges are represented.
If splines=true, edges are drawn as splines routed around nodes; if
splines=false, edges are drawn as line segments. If splines=none or
splines="", no edges are drawn at all.
(1 March 2007) splines=line and splines=spline can be
used as synonyms for splines=false and splines=true, respectively.
In addition, splines=polyline specifies that edges should be drawn as
polylines.
(28 Sep 2010) splines=ortho specifies edges should be
routed as polylines of axis-aligned segments. Currently, the routing
does not handle ports or, in dot, edge labels.
(25 Sep 2012) splines=curved specifies edges should be drawn as curved
arcs.
 |
 |
| splines=none splines="" |
splines=line splines=false |
 |
 |
| splines=polyline | splines=curved |
 |
 |
| splines=ortho | splines=spline splines=true |
By default, splines is unset. How this is interpreted depends on
the layout engine. For dot, the default is to draw edges as splines. For all
other layouts, the default is to draw edges as line segments.
Note that for these latter layouts, if splines="true", this
requires non-overlapping nodes (cf. overlap).
If fdp is used for layout and splines="compound", then the edges are
drawn to avoid clusters as well as nodes.
- Graphs
start
type: startType, default: ""
Parameter used to determine the initial layout of nodes.
If unset, the nodes are randomly placed in a unit square with the same seed is always used for the random number generator, so the initial placement is repeatable.
Valid on:- Graphs
style
type: style, default: ""
Set style information for components of the graph.
For cluster subgraphs, if style="filled", the cluster box’s background is
filled.
If the default style attribute has been set for a component, an individual
component can use style="" to revert to the normal default. For example, if
the graph has
making all edges invisible, the b->c edge can overrride this via:
Of course, the component can also explicitly set its style attribute to the desired value.
- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
stylesheet
type: string, default: ""
A URL or pathname specifying an XML style sheet, used in SVG output.
Combine with class to style elements using CSS selectors.
See also:
Valid on:- Graphs
tail_lp
type: point
Position of an edge’s tail label, in points.
The position indicates the center of the label.
Valid on:- Edges
tailclip
type: bool, default: true
If true, the tail of an edge is clipped to the boundary of the tail node; otherwise, the end of the edge goes to the center of the node, or the center of a port, if applicable.
Valid on:- Edges
tailhref
type: escString, default: ""
Synonym for tailURL.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
taillabel
type: lblString, default: ""
Text label to be placed near tail of edge.
See limitation.
Valid on:- Edges
tailport
type: portPos, default: center
Indicates where on the tail node to attach the tail of the edge.
See limitation.
Valid on:- Edges
tailtarget
type: escString, default: <none>
If the edge has a tailURL, tailtarget determines which
window of the browser is used for the URL.
Setting tailtarget=_graphviz will open a new window if it doesn’t already
exist, or reuse it if it does.
If undefined, the value of the target is used.
- Edges
tailtooltip
type: escString, default: ""
Tooltip annotation attached to the tail of an edge.
Used only if the edge has a tailURL attribute.
- Edges
tailURL
type: escString, default: ""
If defined, tailURL is output as part of the tail label of the
edge.
Also, this value is used near the tail node, overriding any
URL value.
See limitation.
See also:
Valid on:- Edges
target
type: escString | string, default: <none>
If the object has a URL, this attribute determines which window of the browser is used for the URL.
See W3C documentation.
Valid on:- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
tooltip
type: escString, default: ""
Tooltip (mouse hover text) attached to the node, edge, cluster, or graph.
If tooltip is unset, Graphviz will use the object’s label if defined.
Note
that if the label is a record specification or an HTML-like label, the
resulting tooltip may be unhelpful. In this case, if tooltips will be
generated, the user should set a tooltip attribute explicitly.
See also:
Valid on:- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
truecolor
type: bool
Whether internal bitmap rendering relies on a truecolor color model or uses a color palette.
If truecolor is unset, truecolor is not used
unless there is a shapefile property
for some node in the graph.
The output model will use the input model when possible.
Use of color palettes results in less memory usage during creation of the bitmaps and smaller output files.
Usually, the only time it is necessary to specify the truecolor model
is if the graph uses more than 256 colors.
However, if one uses bgcolor=transparent with
a color palette, font
antialiasing can show up as a fuzzy white area around characters.
Using truecolor=true avoids this problem.
- Graphs
URL
type: escString, default: <none>
Hyperlinks incorporated into device-dependent output.
At present, used in ps2, cmap, i*map and svg formats.
For all these formats, URLs can be attached to nodes, edges and
clusters. URL attributes can also be attached to the root graph in ps2,
cmap and i*map formats. This serves as the base URL for relative URLs in the
former, and as the default image map file in the latter.
For svg, cmapx and imap output, the active area for a node is its
visible image.
For example, an unfilled
node with no drawn boundary will only be active on its label.
For other output, the active area is its bounding box.
The active area for a cluster is its bounding box.
For edges, the active areas are small circles where the edge contacts its head
and tail nodes. In addition, for svg, cmapx and imap, the active area
includes a thin polygon approximating the edge. The circles may
overlap the related node, and the edge URL dominates.
If the edge has a label, this will also be active.
Finally, if the edge has a head or tail label, this will also be active.
For edges, the attributes headURL,
tailURL, labelURL and
edgeURL allow control of various parts of an
edge.
if active areas of two edges overlap, it is unspecified which area dominates.
See also:
- Clusters
- Edges
- Graphs
- Nodes
vertices
type: pointList
Sets the coordinates of the vertices of the node’s polygon, in inches.
Used if the node is polygonal, and output is dot or xdot.
If the node is an ellipse or circle, the samplepoints
attribute affects the output.
- Nodes
viewport
type: viewPort, default: ""
Clipping window on final drawing.
viewport supersedes any size attribute. The width and height
of the viewport specify precisely the final size of the output.
- Graphs
voro_margin
type: double, default: 0.05, minimum: 0.0
Factor to scale up drawing to allow margin for expansion in
Voronoi technique. dim' = (1+2*margin)*dim.
- Graphs
weight
type: int | double, default: 1, minimum: 0(dot,twopi), 1(neato,fdp)
Weight of edge.
In dot, the heavier the weight, the shorter, straighter and more vertical the edge is.
For twopi, weight=0 indicates the edge should not be used in
constructing a spanning tree from the root.
For other layouts, a larger weight encourages the layout to make the edge
length closer to that specified by the len attribute.
Weights in dot must be integers.
- Edges
width
type: double, default: 0.75, minimum: 0.01
Width of node, in inches.
This is taken as the initial, minimum width of the node. If
fixedsize is true, this will be the final width of the
node. Otherwise, if the node label requires more width to fit, the node’s
width will be increased to contain the label.
If the output format is dot, the value given to width will be the final
value.
If the node shape is regular, the width and height are made identical:
- If either the width or the height is set explicitly, that value is used.
- If both the width or the height are set explicitly, the maximum of the two values is used.
- If neither is set explicitly, the minimum of the two default values is used.
- Nodes
xdotversion
type: string
Determines the version of xdot used in output.
Only used for xdot output.
If unset, graphviz will set this attribute to the xdot version used for output.
- Graphs
xlabel
type: lblString, default: ""
External label for a node or edge.
- For nodes, the label will be placed outside of the node but near it.
- For edges, the label will be placed near the center of the edge. This can be useful in dot to avoid the occasional problem when the use of edge labels distorts the layout.
- For other layouts, the
xlabel attribute can be viewed as a synonym for the
labelattribute.
These labels are added after all nodes and edges have been placed.
The labels will be placed so that they do not overlap any node or label. This
means it may not be possible to place all of them. To force placing all of
them, set forcelabels=true.
- Edges
- Nodes
xlp
type: point
Position of an exterior label, in points.
The position indicates the center of the label.
Valid on:- Edges
- Nodes
z
type: double, default: 0.0, minimum: -MAXFLOAT, -1000
Deprecated: Use pos attribute, along with
dimen and/or dim to specify dimensions.
Provides z coordinate value for 3D layouts and displays. If the graph has
dim set to 3 (or more), neato will use a node’s z value for
the z coordinate of its initial position if its pos attribute
is also defined.
Even if no z values are specified in the input, it is necessary to
declare a z attribute for nodes, e.g, using node[z=""] in order to get
z values on output. Thus, setting dim=3 but not declaring z will cause
neato -Tvrml to layout the graph in 3D but project the layout onto the
xy-plane for the rendering. If the z attribute is declared, the final
rendering will be in 3D.
- Nodes